'use client'
'use client' lets you mark what code runs on the client.
Reference
'use client'
Add 'use client' at the top of a file to mark the module and its transitive dependencies as client code.
'use client';
import { useState } from 'react';
import { formatDate } from './formatters';
import Link from './link';
export default function RichTextEditor(props) {
formatDate();
// ...
return
<Link />
// ...
}When a file marked with 'use client' is imported from a Server Component, compatible bundlers will treat the module import as a boundary between server-run and client-run code.
As a dependency of RichTextEditor, formatDate and Link will also be evaluated on the client regardless if their modules contain a 'use client' directive.
Deep Dive
React’s full-stack architecture vision is realized through the React Server Components (RSC) specification.
React Server Components lets you coordinate which components of your render tree are rendered on the server or on the client. Server rendering is traditionally more performant and allows access to the back-end, while client rendering is necessary for adding interactivity into your components.
To use React Server Components, you need to use a compatible React framework. These frameworks will render your app on the server by default, unless specified otherwise.
Marking client code with 'use client'
In a React app, components are often split into separate files, or modules.
For apps that use React Server Components, the app is server-rendered by default. 'use client' introduces a server-client boundary in the module dependency tree, effectively creating a client-module subtree.
To better illustrate this, consider the following React Server Component app and its module dependency and render tree.
import FancyText from './FancyText'; import InspirationGenerator from './InspirationGenerator'; import Copyright from './Copyright'; export default function App() { return ( <> <FancyText title text="Get Inspired App" /> <InspirationGenerator> <Copyright year={2004} /> </InspirationGenerator> </> ); }
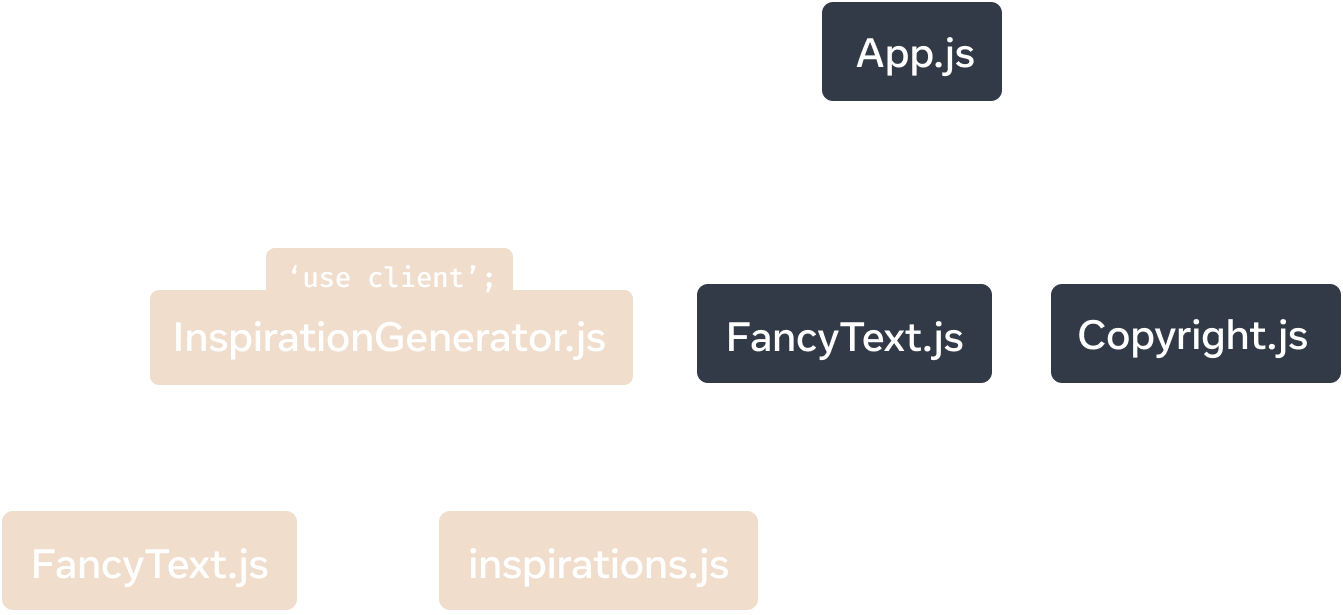

'use client' segments the module dependency tree of the React Server Components app to mark InspirationGenerator.js and any of its dependencies as client-rendered.
In the module dependency tree of the example app, the 'use client' directive in InspirationGenerator.js marks that module and all of its transitive dependencies as client modules. It creates a subtree of client modules with InspirationGenerator.js as the root.
During render, the framework will server-render the root component and continue through the render tree, opting-out of evaluating any code imported from client-marked code.
The server-rendered portion of the render tree is then sent to the client. The client, with its client code downloaded, then completes rendering the rest of the tree.
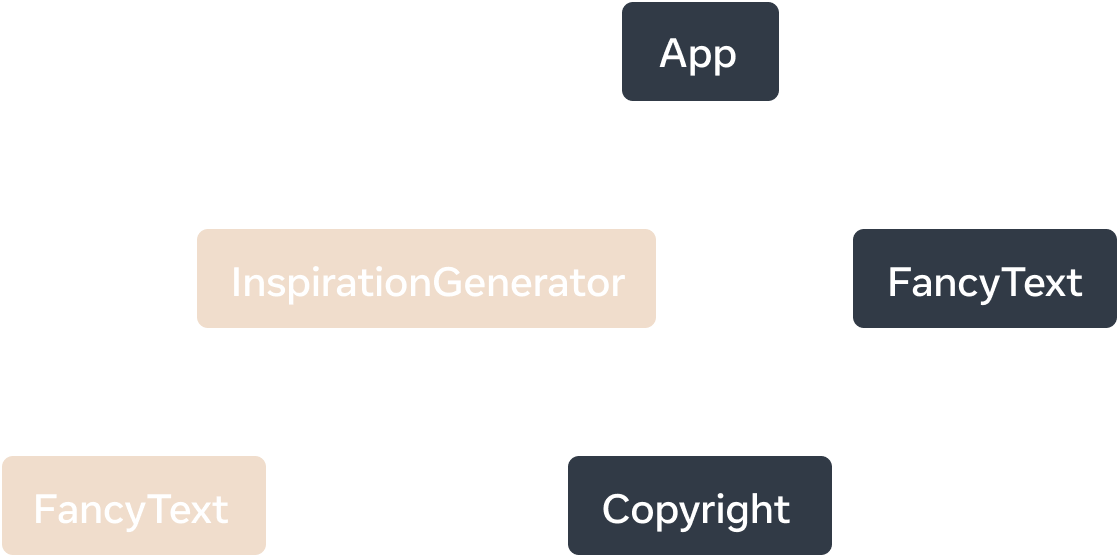
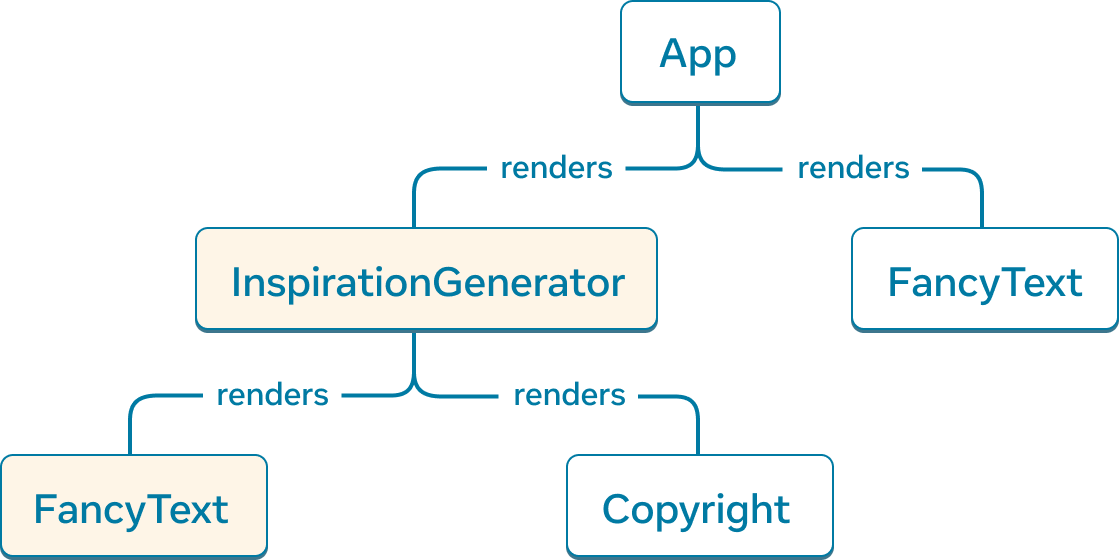
The render tree for the React Server Components app. InspirationGenerator and its child component FancyText are components exported from client-marked code and considered Client Components.
We introduce the following definitions:
- Client Components are components in a render tree that are rendered on the client.
- Server Components are components in a render tree that are rendered on the server.
Working through the example app, App, FancyText and Copyright are all server-rendered and considered Server Components. As InspirationGenerator.js and its transitive dependencies are marked as client code, the component InspirationGenerator and its child component FancyText are Client Components.
Deep Dive
By the above definitions, the component FancyText is both a Server and Client Component, how can that be?
First, let’s clarify that the term “component” is not very precise. Here are just two ways “component” can be understood:
- A “component” can refer to a component definition. In most cases this will be a function.
// This is a definition of a component
function MyComponent() {
return <p>My Component</p>
}- A “component” can also refer to a component callsite of its definition.
import MyComponent from './MyComponent';
function App() {
// This is a usage of a component
return <MyComponent />;
}Often, the imprecision is not important when explaining concepts, but in this case it is.
When we talk about Server or Client Components, we are referring to component callsites.
- If the component is defined in a module with a
'use client'directive, or the component is imported and called in a Client Component, then the component callsite is a Client Component. - If the component is imported and called in a Server Component, then the component callsite is a Server Component.


Back to the question of FancyText, we see that the component definition does not have a 'use client' directive and it has two callsites.
The callsite of FancyText as a child of App, marks that usage as a Server Component as root components are always Server Components. When FancyText is imported and called under InspirationGenerator, that callsite of FancyText is a Client Component as InspirationGenerator is a Client Component since it contains a 'use client' directive.
This means that the component definition for FancyText will both be evaluated on the server and also downloaded by the client to render its Client Component usage.
Deep Dive
As a child of InspirationGenerator, a Client Component, why is Copyright a Server Component?
To clarify, 'use client' defines the boundary between server and client code on the module dependency tree, not the render tree.
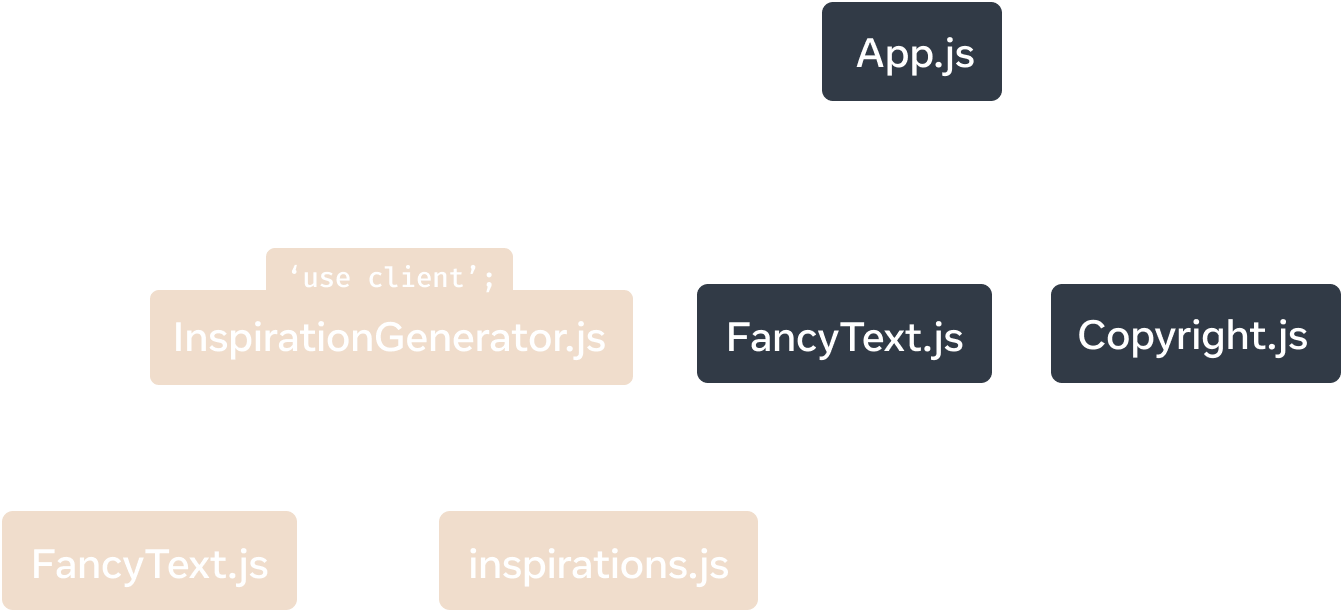
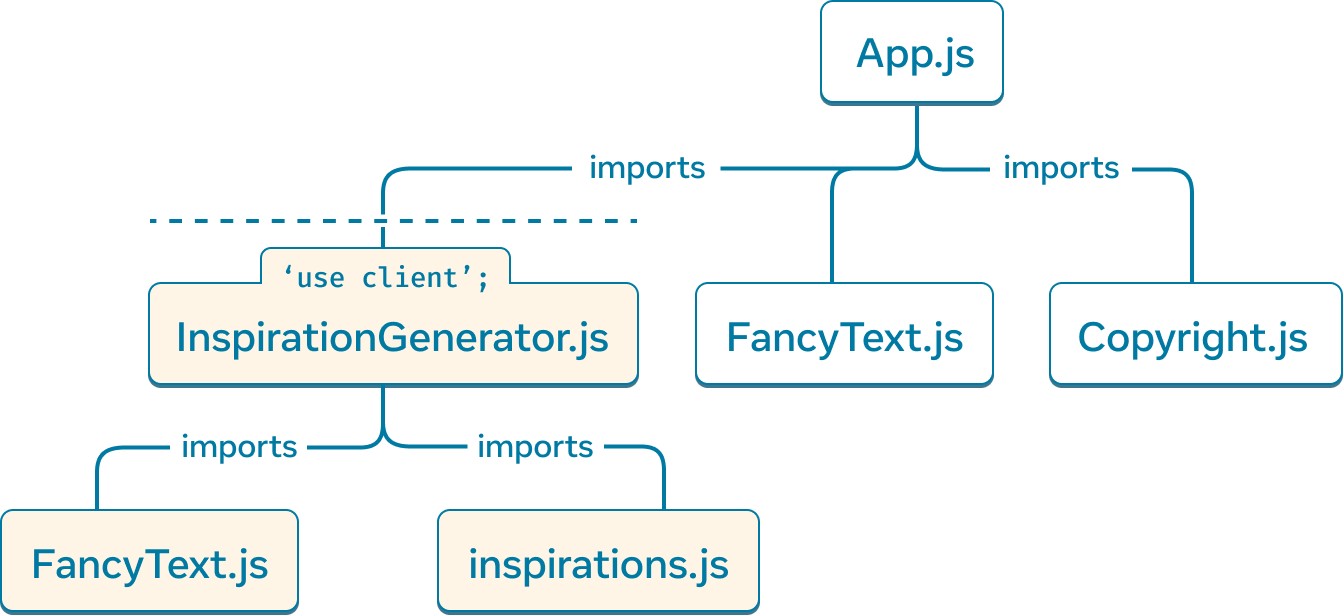
'use client' defines the boundary between server and client code on the module dependency tree.
In the module dependency tree, we see that App.js imports and calls Copyright from the Copyright.js module. As Copyright.js does not contain a 'use client' directive, the component callsite is rendered on the server. App is rendered on the server as it is the root component.
Client Components can render Server Components because you can pass JSX as props. In this case, InspirationGenerator takes JSX as children props and receives Copyright as a children prop. However, the InspirationGenerator module never directly imports the Copyright module nor calls the component, all of that is done by App.
The takeaway is that a parent-child render relationship between components does not guarantee the same render environment.
Server Component advantages and limitations
With 'use client', you can determine what components will be Server or Client Components. To understand when to use Client Components, here is an overview of the advantages and limitations to Server Components.
For simplicity, we talk about Server Components, but the same principles apply to all code in your app that is server run.
Advantages
- Server Components reduce the amount of code sent and run by the client. Only client modules are bundled and evaluated by the client.
- Server Components benefit from running on the server. They can access the local filesystem and may experience low latency for data fetches and network requests.
Limitations
- Server Components cannot support interaction as event handlers must be registered and triggered by a client.
- The browser, as an example client, is responsible for delegating UI clicks to the appropriate
onClickhandler.
- The browser, as an example client, is responsible for delegating UI clicks to the appropriate
- Server Components cannot use most Hooks.
- When Server Components are rendered, they are conceptually resolved into instructions for the client to interpret and turn into UI primitives. This means that Server Components do not persist in memory after render and do not support re-rendering or state.
Passing props from Server to Client Components
As in any React app, parent components pass data to child components. As they are rendered in different environments, passing data from a Server Component to a Client Component requires extra consideration.
Prop values passed from a Server Component to Client Component must be serializable.
Serializable props include:
- Primitives
- Iterables
- Plain objects, those created with object initializers, with serializable properties
- Client or Server Components
- Promises
Notably, these are not supported:
- Functions that are not exported from client-marked modules or marked with
'use server' - Classes
- Objects that are not an instance of Object, or null-prototype objects
- Symbols not registered globally, ex.
Symbol('my new symbol')
Caveats
'use client'must be at the very beginning of a file, above any imports or other code (comments are OK). They must be written with single or double quotes, but not backticks.- When a
'use client'module is imported from another client-rendered module, the directive has no effect. - When a component module contains a
'use client'directive, any usage of that component is guaranteed to be a Client Component. However, a component can still be evaluated on the client even if it does not have a'use client'directive.- A component usage is considered a Client Component if it is defined in module with
'use client'directive or it is a transitive dependency of a module that contains a'use client'directive. Otherwise, it is a Server Component.
- A component usage is considered a Client Component if it is defined in module with
- Code that is marked for client evaluation is not limited to components. All code that is a part of the client module sub-tree is sent to and run by the client.
- When a server evaluated module imports values from a
'use client'module, the values must either be a React component or supported serializable prop values to be passed to a Client Component. Any other use case will throw an exception.
Usage
Building with interactivity and state
'use client'; import {useState} from 'react'; export default function Counter({initialValue = 0}) { const [countValue, setCountValue] = useState(initialValue); const increment = () => setCountValue(countValue + 1); const decrement = () => setCountValue(countValue - 1); return (<> <h2>Count Value: {countValue}</h2> <button onClick={increment}>+1</button> <button onClick={decrement}>-1</button> </>); }
As Counter requires both the useState hook and event handlers to increment or decrement the value, this component must be a Client Component and will require a 'use client' directive at the top.
In contrast, a component that renders UI without interaction will not need to be a Client Component.
import {getCounterValueFromFile} from 'fs-utils';
import Counter from './Counter';
export default async function CounterContainer() {
const initialValue = await getCounterValueFromFile();
return <Counter initialValue={initialValue} />
}For example, the parent component of the Client Component CounterContainer does not require 'use client' as it is not interactive and does not use state. To be more specific, CounterContainer must be a Server Component as it reads from the local file system on the server. Notably, Server Components support asynchronous rendering, which is not supported for Client Components.
There are also components that don’t use any server or client-only features and can be agnostic to where they render. FancyText is an example of such a component.
export default function FancyText({title, text}) {
return title
? <h1 className='fancy title'>{text}</h1>
: <h3 className='fancy cursive'>{text}</h3>
}In this case, it is discouraged to use the 'use client' directive as it pre-maturely forces all component usages of FancyText to be rendered on the client, which comes at a performance cost. As demonstrated in the earlier Inspirations app example, FancyText is used as both a Server or Client Component, depending on where it is imported and used.
Using client APIs
Your React app may use client-specific APIs which are dependent on your targeted client. For the browser, some example client APIs include web storage, audio and video manipulation, device hardware, among others.
In this example, the component references the canvas element and DOM through the ref. Both of which are only accessible on the browser so this component must be marked as a Client Component.
'use client';
import {useRef, useEffect} from 'react';
export default function Circle() {
const ref = useRef(null);
useLayoutEffect(() => {
const canvas = ref.current;
const context = canvas.getContext('2d');
context.beginPath();
context.arc(100, 75, 50, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
context.stroke();
});
return <canvas ref={ref} />
}Using React libraries
Often in a React app, you’ll leverage third-party libraries to handle common UI patterns or logic.
These libraries may rely on component Hooks or client APIs. In these cases, you’ll need to ensure you’re using these libraries in Client Components. Depending on the nature of these libraries, this may mean adding a 'use client' near the top of your module dependency tree – marking the majority of your React app as client-rendered.
Libraries that use any of the following React APIs must be marked as client-run:
- createContext
reactandreact-domHooks- forwardRef
- memo
- startTransition
- If they use client APIs, ex. DOM insertion or native platform views